About Idaho Copper
Idaho Copper
Idaho Copper
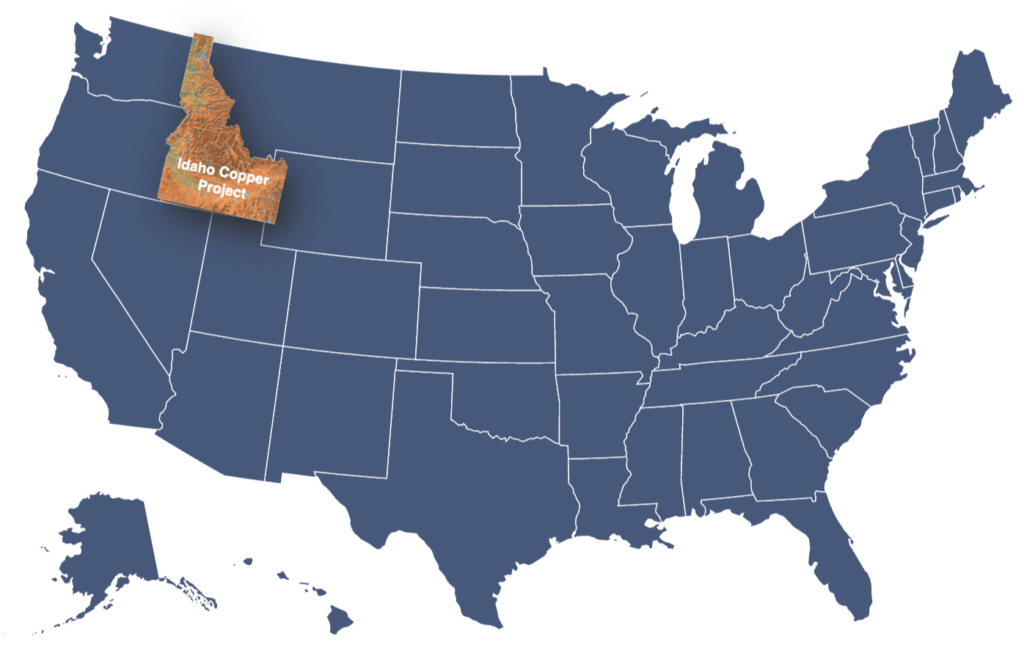
Idaho Copper (“IC”) seeks to capitalize on the looming copper supply deficit by advancing one of the largest untapped copper projects in the United States. The economics of the project benefit from extensive high-value co-products including molybdenum and silver.
IC is committed to conducting all exploration and development activities, present and future, in a manner that ensures a minimal impact on the environment. Every decision made by the development team is focused on designing an environmentally sound and socially responsible project.
IC subscribes to the philosophy that a long-term approach to business sustains a profitable exploration and development company. The resource industry can be extremely volatile and inherently impacts local and regional economies, environments and invested social groups. By strictly adhering to sustainable development principles, IC is investing in the long-term economic health of the company.
This lifecycle approach to business aims to leave a net positive imprint or, at the very least, a neutral impact on the geographic areas and lives touched by each of its projects. The company is committed to renewed production of minerals and the responsible development of natural resources by using regulatory and cost-benefit analysis tools to achieve balance on economic, environmental and social bottom lines.
Idaho Copper
Idaho Copper (“IC”) seeks to capitalize on the looming copper supply deficit by advancing one of the largest untapped copper projects in the United States. The economics of the project benefit from extensive high-value co-products including molybdenum and silver.
IC is committed to conducting all exploration and development activities, present and future, in a manner that ensures a minimal impact on the environment. Every decision made by the development team is focused on designing an environmentally sound and socially responsible project.
IC subscribes to the philosophy that a long-term approach to business sustains a profitable exploration and development company. The resource industry can be extremely volatile and inherently impacts local and regional economies, environments and invested social groups. By strictly adhering to sustainable development principles, IC is investing in the long-term economic health of the company.
This lifecycle approach to business aims to leave a net positive imprint or, at the very least, a neutral impact on the geographic areas and lives touched by each of its projects. The company is committed to renewed production of minerals and the responsible development of natural resources by using regulatory and cost-benefit analysis tools to achieve balance on economic, environmental and social bottom lines.
Advancing strategic mineral projects through responsible practices and sustainable development
Idaho Copper is still in the exploration and feasibility phase and therefore, the Company has not yet adopted any ESG metrics. However, we acknowledge the value of maintaining good social and governance principles. As such, we strictly adhere to all environmental permitting requirements and continue to have a high degree of stakeholder engagement with local communities.
Environment
Social
Governance
Critical Minerals Advocacy
The US Critical Minerals list is compiled every three years by the United States Geological Survey, with a goal of identifying commodities that have “important uses and no viable substitutes, yet face potential disruption in supply, and are considered critical to the Nation’s economic and national security.” For a mining project, having minerals on this list can lead to enhanced cooperation from government officials and a more streamlined permitting process.
Molybdenum (moly) is a logical candidate for inclusion on the US critical minerals list, and Idaho Copper is taking a leading role in lobbying for its inclusion. It is vital for US defense, where it is an ingredient in lubricants, fortifies the steel used in US tanks, and is important in jet engine components. More broadly, it is an alloy that is critical in steel production, especially stainless and other value-added steels.
Presently China controls 56% of the world’s molybdenum production, with the US at only 18%. As the US moves toward self-sufficiency with respect to resources, moly is one of numerous minerals where a disruption in foreign supplies could cripple the US economy. To address this vulnerability, the US should follow the lead of Canada and the UK, both of which have included moly on their critical mineral lists.
Copper is a cornerstone of modern infrastructure and an essential element of the clean energy transition. Electric vehicles require four times more copper than conventional cars, a single wind turbine uses nearly five tons, and solar demand is projected to increase copper use by more than 60-fold by 2040. Beyond renewable energy, copper is vital for electrical wiring, grid expansion, AI data centers, and national defense.
The U.S. imported 46% of its copper consumption in 2023, up sharply from 37% in 2019, underscoring the country’s growing reliance on foreign suppliers. Recognizing this vulnerability, the U.S. Geological Survey has proposed adding copper to the federal Critical Minerals list. Such a designation would highlight copper’s importance to economic and national security while creating pathways for streamlined permitting and potential access to federal grants. With one of the largest undeveloped copper resources in the United States, Idaho Copper is well positioned to contribute meaningfully to a secure domestic supply.
Silver is more than a precious metal – it is a strategic industrial mineral with unmatched conductive and antimicrobial properties. It is essential in the production of solar panels, advanced electronics, semiconductors, and medical technologies, all of which are critical to U.S. defense and clean energy infrastructure.
The U.S. Geological Survey has proposed adding silver to the Critical Minerals list, reflecting its increasingly vital role in both national defense and the global energy transition. The CuMo Project contains nearly 180 million ounces of measured and indicated silver resources, making Idaho Copper one of the largest potential domestic contributors to U.S. silver supply. By responsibly developing this resource, Idaho Copper can help reduce reliance on foreign imports and strengthen the nation’s resilience in critical industries.
Rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth’s crust and is critical to national defense and advanced energy technologies. It is a key alloying agent in superalloys used for jet engines, gas turbines, and other high-temperature aerospace applications where strength and resistance to heat are paramount. Its scarcity and lack of substitutes make rhenium strategically important to both defense and energy security.
Global rhenium production is limited, with much of the supply concentrated outside the United States. The CuMo Project contains potentially recoverable rhenium as a co-product, providing Idaho Copper with an opportunity to contribute to securing domestic rhenium supply. With the U.S. government actively supporting projects that strengthen critical mineral supply chains, rhenium resources at CuMo enhance the project’s strategic importance and potential eligibility for federal support.
Tungsten is prized for its exceptional density, hardness, and highest melting point of all metals, making it indispensable in defense, aerospace, and advanced manufacturing. It is used in armor-piercing projectiles, cutting tools, drilling equipment, and electronics. Tungsten’s unique properties mean that few materials can replace it, and global supply disruptions would directly impact industries critical to U.S. security.
China currently dominates the global tungsten market, producing the majority of world supply. This dependency has been identified as a strategic risk for the U.S., where tungsten is designated as a critical mineral. The CuMo Project contains significant quantities of tungsten as a byproduct, positioning Idaho Copper to play a meaningful role in diversifying U.S. supply. As the federal government expands support for domestic critical mineral projects, tungsten production from CuMo could help safeguard U.S. defense and industrial capabilities.
Policy Positions
The National Strategic and Critical Minerals Production Act (H.R. 520 & S.B.145) introduced by Rep. Mark Amodei (NV.) and Sen. Dean Heller (NV) could shorten the mine permitting process by providing:
- Efficient, timely and thorough permit reviews.
- Incorporating best practices for coordination among state and federal agencies.
- Clarifying responsibilities in an effort to avoid duplication.
- Setting binding timeframes.
In March 2018, the bill passed in the House Natural Resources Committee, signaling a bipartisan appeal for change.
Congress, recognizing the inefficiency in permitting for infrastructure projects, enacted FAST 41. FAST 41 was designed to improve the timeliness, predictability, and transparency of the Federal environmental review and authorization process for covered infrastructure projects
The primary purpose of FAST 41 is to:
- Encourage coordination between government agencies.
- Increase transparency of the permitting process.
- Improve accountability on delayed projects.
Oversight hearings in the US Senate indicate that the Congress is open to discussion to consider other projects in this definition. Idaho CuMo has joined other industry and association leaders to encourage Congress to designate mining projects as “infrastructure projects” under FAST 41 in an effort to reduce permitting times, decrease foreign dependence on strategic minerals and metals, and shore up our Nation’s economy and infrastructure.
The United States Geological Survey needs to be refocused to its core mission of maintaining geological and geophysical surveying; and mapping and maintaining ongoing inventories of our Nation’s mineral resources.
The lack of electronically accessible, up-to-date topographical, geological, and geophysical data has negatively affected our nation’s ability to explore, find and produce strategic and critical minerals essential to our Nation’s economic well-being and national security.
The Open Book on the Equal Access for Justice Act was introduced by Rep. Doug Collins (R-GA) and Sen. John Barrasso, and became law in March, 2021. The Act establishes a database to track litigation against the US because, according to Congresswoman Cynthia Lumis (R-WY), “large environmental groups have hijacked EAJA into a means to perpetually fund a cottage industry based upon suing the federal government over and over again… creating a bottomless, untraceable money pit to push their political agenda.”
The 2018 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) contains three provisions added by the U.S. House of Representatives to shore up our Nation’s national defense and decrease our foreign reliance on non-allied countries for critical minerals and metals.
- Section 873 prohibits procurement of defense sensitive material from non-allied nations.
- Section 343 mandates that copper, molybdenum, gold, nickel, lead, silver, and certain compounds found in fertilizers, be added to the critical minerals list.
- Representative Amodei (NV) amended the NDAA to significantly reduce mine permitting processes from ten years to two.
The NDAA passed the House with all three provisions, but the Senate passed it without the above provisions. The NDAA will now head to negotiation conferences between the Senate and the House.
Advancing strategic mineral projects through responsible practices and sustainable development
Idaho Copper is still in the exploration and feasibility phase and therefore, the Company has not yet adopted any ESG metrics. However, we acknowledge the value of maintaining good social and governance principles. As such, we strictly adhere to all environmental permitting requirements and continue to have a high degree of stakeholder engagement with local communities.
Environment
“The company is committed to renewed production of minerals and the responsible development of natural resources . . .”
Idaho Copper is committed to conducting all exploration and development activities, present and future, in a manner that ensures a minimal impact on the environment. By strictly adhering to sustainable development principles, IC is investing in the long-term economic health of the company.
Social
“. . . the highest degree of integrity throughout all stages of exploration and development . . .”
Idaho Copper incorporates incentives for local operators to build relationships and run environmentally and socially responsible operations. The company believes that it is always in the best interest of local communities, business partners and shareholders, to maintain the highest degree of integrity throughout all stages of exploration and development.
Governance
“there is a balance between the conventional wisdom about the business of mining, and the company’s responsibility to steward sustained resource exploration and production.”
Idaho Copper management considers financial feasibility, economic reward, stakeholder input, and environmental impacts, at all levels of exploration and development. Management always strives to reconcile economic and social development opportunities with the need for conservation and environmental protection.